AoI-Driven IoT Fault Detection for Smart Grids
Ensuring the reliability of modern electric distribution grids requires real-time monitoring systems that can detect faults quickly and efficiently. Traditional IoT-based fault detection often suffers from network congestion, redundant transmissions, and delayed updates, leading to stale data and reduced responsiveness. To overcome these challenges, this study introduces the first Age of Information (AoI)-driven IoT fault detection system for smart grids.
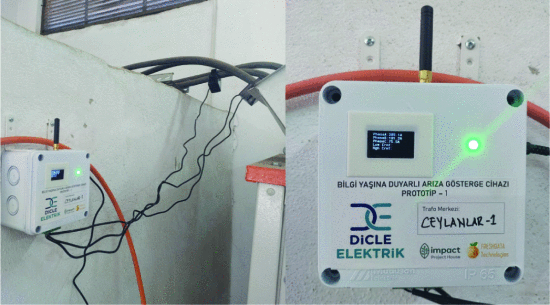
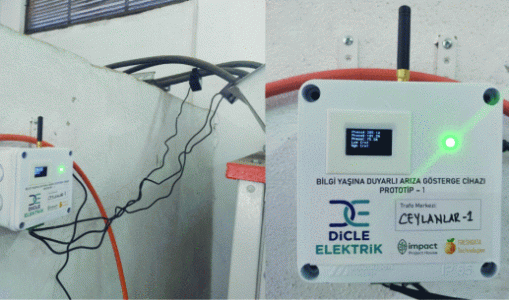
AoI-driven IoT fault detection device on a transformer.
The proposed system uses an AoI-optimized algorithm that dynamically adjusts data transmission intervals, prioritizing critical updates while reducing unnecessary traffic. Built on a dual-processor architecture, STM32 microcontrollers handle real-time current and voltage measurements, while ESP32 modules manage MQTT-based communication with GSM/Wi-Fi connectivity. This separation ensures low-latency fault detection and reliable data freshness.
A complete prototype was deployed across five live transformer stations in collaboration with Dicle Elektrik. The system successfully detected 27 distinct fault types, including single, two, and three-phase faults, as well as broken-wire conditions. Experimental results highlight that the AoI-driven protocol enables timely fault detection with minimal data use—as low as 17 KB/year in fault mode and 55 MB/year in continuous mode—making the solution scalable for battery-powered, long-term IoT deployments.
By integrating semantic communication, anomaly detection, and AoI-aware optimization, the framework delivers a practical, efficient, and adaptive solution for real-world grid monitoring. Future work will focus on extending the system with Age Control Protocols (ACP/ACP+) and A3L-FEC to further enhance timeliness, robustness, and scalability in large-scale smart grid deployments, including potential applications in satellite and remote-area power networks.