WirelessEnergySim: A Discrete Event Simulator for an Energy-Neutral Operation of IoT Nodes
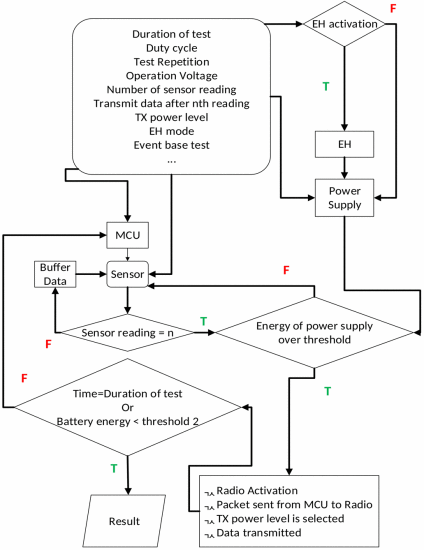
WirelessEnergySim is a discrete-event simulation tool developed to estimate power consumption, energy harvesting, and the operational lifetime of Internet of Things (IoT) nodes operating under energy-neutral conditions. Built upon empirical measurements from wireless sensor nodes equipped with electromagnetic energy harvesters, the simulator models the energy profile of each hardware component, including the microcontroller, radio transceiver, sensor, and LEDs, under varying duty cycles.
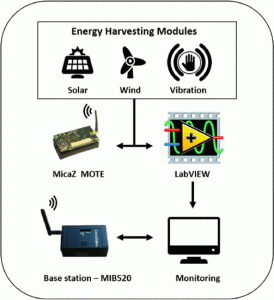
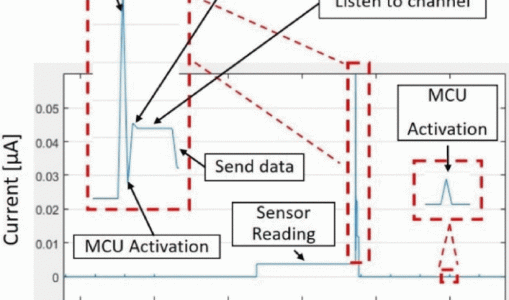
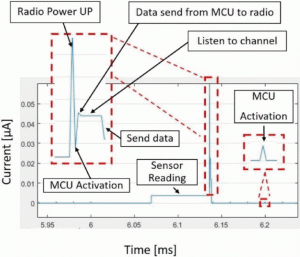
WirelessEnergySim allows for configurable energy harvesting inputs—both deterministic and random—and provides detailed outputs such as current flow variations, energy depletion curves, and component-level energy usage. Through case studies with MicaZ motes and in-house energy harvesting units, the simulator is shown to accurately reflect real-world performance, offering more than 90% agreement with experimental data. Additionally, the simulator supports adaptive transmission strategies, modeling scenarios in which power levels dynamically adjust based on available energy.
The tool provides researchers and engineers with a reliable and scalable method to design and evaluate self-sustaining IoT systems without the need for lengthy and costly field experiments. WirelessEnergySim is especially well-suited for applications in energy-constrained environments such as industrial monitoring, where accurate energy modeling is critical to sustainable operation.